
Go High Level Features: 2025 Complete Guide to Accelerate Your Business
August 28, 2025
AI Teaching Assistant MathGPT.ai Now Adopted by Over 50 Institutions
August 29, 2025Google Cloud Security 2025: Can AI Defenders Stay Ahead?
At Google’s modern Singapore office, Mark Johnston, Director of the Office of the CISO for Asia Pacific, gave journalists a sobering reminder: even after half a century of cybersecurity innovation, defenders remain largely reactive.
“In 69% of breaches across Japan and Asia Pacific, organisations only learned about incidents from external parties,” Johnston noted. The figure highlighted a troubling truth — many businesses still struggle to detect their own compromises.
This set the tone for the “Cybersecurity in the AI Era” roundtable, where Google Cloud unveiled its AI-powered approach to closing long-standing security gaps with Google Cloud Security 2025.
50 Years, Same Problems
The challenge isn’t new. Johnston pointed back to James B. Anderson’s 1972 remark: “Systems that we use really don’t protect themselves.” More than 50 years later, the statement still rings true.
Google Cloud’s threat intelligence reveals that over 76% of breaches stem from simple issues like poor configurations or stolen credentials. A recent Microsoft SharePoint zero-day showed how attackers can repeatedly exploit widely used platforms before patches are applied.
The AI Arms Race
According to Kevin Curran, IEEE senior member and cybersecurity professor, the battle has become a high-stakes AI arms race.
For defenders, AI accelerates anomaly detection, incident response, and vulnerability discovery.
For attackers, AI supercharges phishing, malware creation, and large-scale scanning.
This dual use fuels what Johnston calls the “Defender’s Dilemma” — the same technology meant to protect organisations is also empowering adversaries.
Google’s counter-strategy: deploy AI at scale. With Google Cloud Security 2025, the company is leaning into generative AI for secure coding, automated incident response, advanced threat intel, and vulnerability discovery.
Project Zero’s Big Sleep: AI Uncovers What Humans Miss
One standout example is Google’s Project Zero Big Sleep, which applies large language models to find hidden software vulnerabilities. Johnston revealed that it recently discovered multiple flaws in open-source libraries — marking the first time Google believes AI uncovered vulnerabilities independently.
The pace is accelerating fast: from spotting just one issue last month to identifying 47 vulnerabilities in August alone. This signals a shift toward semi-autonomous security operations, where Google’s Gemini AI shoulders much of the work, escalating only the toughest challenges to human analysts.
Automation’s Double-Edged Sword
Google Cloud’s vision for security operations follows a four-step path: Manual → Assisted → Semi-Autonomous → Fully Autonomous.
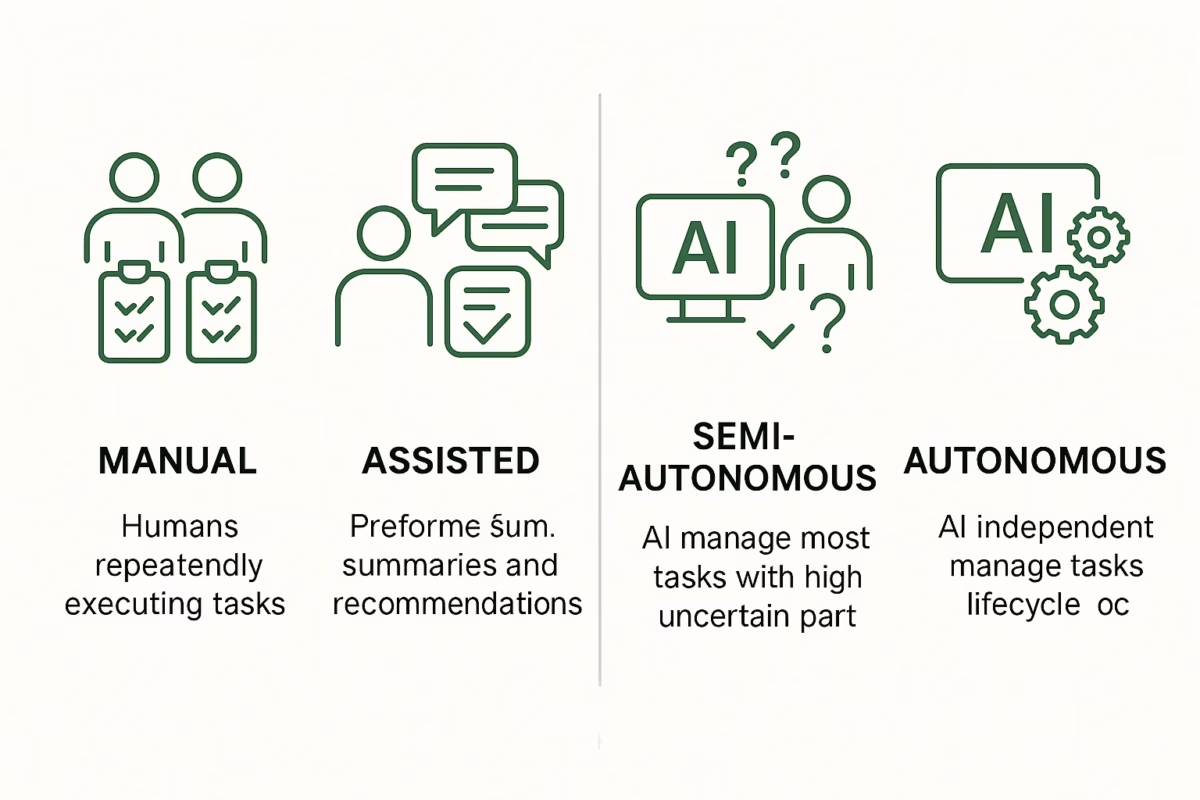
In theory, fully autonomous systems could eventually manage the entire security lifecycle. But Johnston cautioned: “These systems themselves could be attacked or manipulated. Today, there’s no robust framework ensuring they haven’t been tampered with.”
Curran echoed the warning, stressing that human oversight is critical: “A human copilot will remain essential.”
Guardrails for Real-World AI
AI’s unpredictability introduces new risks. A customer chatbot drifting into irrelevant or sensitive advice is just one example. To address this, Google launched Model Armor — a safeguard that filters outputs for relevance, strips sensitive data, and ensures brand-safe responses.
Google is also tackling “shadow AI” — unauthorised AI tools deployed by employees. New cross-environment data protection systems aim to detect and control these hidden risks.
Budgets vs. Rising Threats
Despite increasing threats, CISOs across Asia Pacific face tight budgets. Johnston described the squeeze: “More alerts, more attacks, more complexity — but no additional resources.”
This financial reality raises the stakes for solutions like Google Cloud Security 2025, which promise automation, scalability, and intelligence without major increases in staffing.
Critical Questions for the Future
Even with promising AI advances, questions remain. Johnston admitted: “We haven’t yet seen truly novel AI-powered attacks, but attackers are using AI to scale existing methods.”
Accuracy is another issue. Google says AI tools cut reporting time by 50%, but errors persist. As Johnston put it, “Humans make mistakes too.”
Looking further ahead, Google Cloud is already preparing for post-quantum security, deploying post-quantum cryptography across its data centers to prepare for the quantum era.
Conclusion: Balancing AI Power and Human Oversight
AI is reshaping cybersecurity — offering both breakthrough defenses and new risks. Tools like Big Sleep and Gemini are giving defenders unprecedented capabilities, but adversaries are just as eager to exploit the same technologies.
Curran’s closing words summed it up: “Cyberattacks are a matter of ‘when,’ not ‘if.’ AI will only multiply the opportunities available to threat actors.”







